sodium chloride 0.9%
 Saline (medicine) - Wikipedia
Saline (medicine) - WikipediaSodium Chloride 0.9% Intravenous BP Infusion Ingredient activeCategoria legalPOM: Medicine by prescription Last Updated at emc: 24 Dec 2018 Show Table of Contents Hide Table of Contents This information is intended for health professionals Sodium Chloride 0.9% Intravenous Infusion BPSodium Cloride: 9.0 g/lEach ml contains sodium chloride 9 mg. mmol/l: Na+ : 154 Cl-: 154. mmol/l: Na+ : 154 Cl-: 154. pH: 4.5 -7For the complete list of the excipients: see section 6.1Solution for infusion Skin solution, free of visible particles. Sodium Chloride 0.9% intravenous infusion is indicated for: • Treatment of extracellular isotonic dehydration • Treatment of Sodium Depletion • Vehicle or dilution of medications compatible for parenteral administration. Posology Adults, elders and children: The doses can be expressed in terms of sodium mEq or mmol, sodium mass or sodium salt mass (1 g NaCl = 394 mg, 17.1 mEq or 17.1 mmol of Na and Cl). Fluid equilibrium, serum electrolytes and acid-base balance should be monitored before and during administration, with special attention to serum sodium in patients with increased vasopressin non-osmotic release (inappropriate anti-diauretic hormone secretion syndrome, SIADH) and in co-medicated patients with vasopressin agonist drugs, due to the risk of hospital acquired hyponatraemia sections 4 and 4.5.4. Surveillance of the serum sodium is particularly important for hypothonic fluids. Sodium Chloride 0.9% intravenous infusion has a tonic of 308 mOsm/l (approx.) The infusion rate and volume depend on age, weight, clinical condition (e.g. burns, surgery, head injuries, infections), and concomitant therapy should be determined by the experienced consultant physician in intravenous fluid therapy (see sections 4.4 and 4.8). Recommended dose The recommended dose for the treatment of extracellular isotonic dehydration and the depletion of sodium is: • For adults: 500 ml to 3 litres/24h • For babies and children: 20 to 100 ml per 24h and per kg of body weight, depending on the age and total body mass. The recommended dose when used as a vehicle or diluted varies from 50 to 250 ml per dose of medicinal product to be administered. When Sodium Chloride 0.9% is used as a diluent for injecting other medications, the dose and infusion rate will also be dictated by the nature and dose regime of the prescribed medication. Management method The solution is intravenous infusion management through a range of sterile and non-pyrogenic administration, using aseptic technique. The equipment should be prepared with the solution to prevent the air from entering the system. The product must be visually inspected for particle matter and discoloration before administration. Do not administer unless the solution is clear, free of visible particles and the seal is intact Do not remove the overwrap unit until it is ready for use. The internal bag maintains the sterility of the solution. Manage immediately after inserting the infusion set. Do not connect flexible plastic containers in series to avoid air embolism due to the possible residual air contained in the primary container. Pressing intravenous solutions contained in flexible plastic containers to increase flow rates can result in air embolism if the residual air in the container is not completely evacuated before the administration. The use of an intravenous management vented with the vent in an open position could lead to aerial embolism. Intravenous management assemblies ventilated with the vent in an open position should not be used with flexible plastic containers. Additives can be introduced before infusion or during infusion through the injection site. For information on incompatibility and product preparation (with additives), see sections 6.2 and 6.6. The solution is contraindicated in patients with hypernatraemia or hyperchloroemia. Contraindications related to the medicinal product added should be considered. Fluid salt / kidney function Fluid salt / kidney function Use in patients with kidney disabilities (severa) Sodium Chloride 0.9% should be given with special caution to patients with or at risk of severe kidney impairment. In such patients, the administration of Sodium Chloride 0.9% may result in sodium retention. (See "Use in patients at risk of sodium retention, fluid overload and edema" below; for additional considerations.) Risk of overloading fluid and/or solute and electrolytic alterations Depending on the volume and rate of infusion, the intravenous administration of Sodium Chloride 0.9% can cause: • Fluid overload and/or solute resulting in overhydration/hypervolemia and, for example, congested states, including central and peripheral edema. • Electrolyte disorders of clinical relevance and acid-based imbalance. In general, the risk of dilutional states (water retention relative to sodium) is inversely proportional to the electrolytic concentrations of Sodium Chloride 0.9% and its additions. On the contrary, the risk of overloading of solute that causes congested states (water-related solute retention) is directly proportional to Sodium Chloride's electrolyte concentrations of 0.9% and its additions. Special clinical monitoring is required at the beginning of any intravenous infusion. Clinical evaluations and periodic lab determinations may be necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations and acid-based balance during extended parenteral therapy or when the patient's condition or administration rate warrants such evaluation. High volume infusion should be used under specific monitoring in patients with heart or lung failure and in patients with non-osmotic vasopressin (including SIADH), due to the risk of hyponatraemia acquired by the hospital (see below). Hypotraemia Patients with non-osmotic vasopressin release (e.g. acute disease, pain, postoperative stress, infections, burns and CNS disease), patients with heart, liver, and kidney disease, and patients exposed to vasopressin agonists (see section 4.5) are at particular risk of acute hyponatraemia to the infusion of hypothonic fluids. Acute hyponatraemia can lead to acute hyponatraemic encephalopathy (brainedema) characterized by headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy and vomiting. Patients with cerebral edema are at particular risk of serious, irreversible and life-threatening brain injury. Children, women of childbearing age and patients with lower brain compliance (e.g. meningitis, intracranial bleeding, concussion and cerebral edema) are at a particular risk of serious and potentially fatal brain inflammation caused by acute hyponatraemia. Use in patients at risk of sodium retention, fluid overloading and edema Sodium Chloride 0.9% should be used with special caution, if at all, in patients with or at risk of: • Hypernatraemia. Rapid correction hypernatraemia once adaptation has occurred can result in a brain edema, which could result in seizures, permanent brain damage or death. • Hyperchloroemia • metabolic acidosis, which can worsen by prolonged use of this product, especially in patients with kidney deficiency. • Hypervolaemia may be precipitated as congestive heart failure and pulmonary edema, especially in patients with cardiovascular disease. • Hematogenic hyperchlorogenic metabolic acidosis (e.g. during intravenous volume resuscitation) • Conditions that can cause sodium retention, fluid overloading and edema (central and peripheral), such as patients with primary hyperaldostheronism, secondary hyperaldostheronism, associated, for example, hypertension, congestive heart failure, liver disease (including cirrhosis), kidney disease (including renal arterial stenosis, nephrosclerosis) or pre-eclampsia. Medicines that may increase the risk of sodium and fluid retention, such as corticosteroids Infusion reactions Symptoms of unknown aetiology that may seem to be hypersensitivity have been reported very rarely in association with sodium chloride infusion 0.9 %. These have been characterized as hypotension, pyrexia, tremor, chills, hives, rash and pruritus. Stop infusion immediately if signs or symptoms of these reactions develop. Appropriate therapeutic countermeasures should be instituted as clinically indicated. Groups of specific patients Groups of Specific Patients The consultant doctor should be experienced in the use and safety of this product in these special populations that are especially sensitive to rapid changes in serum sodium levels. Rapid correction of hyponatraemia and hypernatraemia is potentially dangerous (risk of serious neurological complications). See the section "Hyponatraemia/hypernatraemia" above. Pediatric population The concentrations of plasma electrolytes should be closely monitored in the pediatric population, as this population may have a fluid and electrolyte regulation capacity. Therefore, repeated infusions of sodium chloride should only occur after determination of the serum sodium level. Geriatric population When selecting the type of infusion solution and the volume/value of infusion for a geriatric patient, consider that geriatric patients are generally more likely to have heart, kidney, liver, and other diseases or concomitant therapy. For information on product preparation and additives, see Section 6.6. Medicines that lead to greater vasopressin effect The drugs listed below increase the vasopressin effect, leading to a reduction in the excretion of renal electrolyte-free water and may increase the risk of hyponatraemia acquired in hospital after inappropriately balanced treatment with iv fluids (see sections 4.2, 4.4 and 4.8). • The release of the drug-stimulating vasopressin includes: Clorpropamide, clofibrate, carbamazepin, vincristine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, 3.4-methylenedioxy-N-methamphetamine, ifosfamide, antipsychotics, narcotic drugs • Drugs boosting vasopressin action include: Chlorpropamide, NSAIDs, cyclophosphamide • vasopressin analogs include: Desmopressin, oxytocin, terlipressin Other medicinal products that increase the risk of hyponatraemia also include diuretics in general and antiepileptics such as oxcarbazepine. Precaution is advised in patients treated with lithium. Renal sodium and lithium cleansing can be increased during the administration of Sodium Chloride 0.9 per cent. Sodium Chloride administration 0.9% may result in decreased lithium levels. Corticoids and steroids and carbenoxolone are associated with sodium and water retention (with edema and hypertension). See section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use. There is no adequate data on the use of Sodium Chloride 0.9% in pregnant or nursing women. The doctor should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits for each specific patient before administering Sodium Chloride 0.9%. Sodium Chloride 0.9 per cent should be administered with special caution for pregnant women during work, especially with regard to serum-sodium if administered in combination with oxytocin (see paras. 4, 4 and 48). Caution is advised with patients with preeclampsia (see section 4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use). When a medicinal product is added, the nature of the medication and its use during pregnancy and breastfeeding should be considered separately. No studies have been carried out on the influence of Sodium Chloride 0.9% on the ability to operate a car or other heavy machinery. The following adverse reactions have been reported in the post-marketing experience. The frequency of adverse reactions of the drugs listed in this section cannot be estimated from the available data. System Organ Class (SOC) Adverse reactions (Preferred term) Frequency Nervous system disorders Tremor Acute hyponatraemic encephalopathy* You don't know. Metabolism and nutritional disorders Hospital acquired hyponatraemia* You don't know. Vascular disorders Hypotension You don't know. Disorders of skin and subcutaneous tissue Urticaria Rash Pruritus You don't know. General disorders and conditions of the administration site: Infusion site reactions, such as • erythema of the infusion site, • irritation of the vein, screwing the injection site, burning sensation, • Pain or local reaction , infusion site urticaria • Infection at the injection site, • Venous thrombosis or flebitis extending from the injection site, extravasation and hypervolemia • Pirexia • Chills You don't know. System Organ Class (SOC) System Organ Class (SOC) Adverse reactions (Preferred term) Adverse reactions (Preferred term) Frequency Frequency Nervous System Disorders Acute Hyponatraemic Encephalopathy* Metabolism and Nutritional DisordersHospital Acquired Hyponatraemia* You don't know. Vascular disorders Hypotension Not known Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue UrticariaRashPruritus You don't know. General disorders and conditions of the administration site: Infusion site reactions, such as • erythema of the infusion site, • irritation of the vein, screwing the injection site, burning sensation, • Pain or local reaction , infusion site urticaria • Infection at the injection site, • Venous thrombosis or flebitis extending from the injection site, extravasation and hypervolemia • Pirexia • Chills. *Hospital acquired hyponatraemia can cause irreversible brain injury and death, due to the development of acute hyponatrahemic encephalopathy, unknown frequency (see sections 4.2. 4.4, 4.5). The following adverse reactions have not been reported with this product, but may occur: • Hypernatraemia (e.g., when given to patients with insipid nephrogenic diabetes or high blood output) • Hyperchlorocemic metabolic acidosis • Hypotraemia, which can be symptomatic. Hypoatraemia can occur when the normal excretion of free water is deteriorated. (e.g., SIADH or postoperative)The general adverse effects of sodium excess are described in section 4.9 Overdose. Additives When Sodium Chloride 0.9% is used as a diluent for injecting other drugs, the nature of additives will determine the probability of any other undesirable effect. If an adverse event occurs, the patient must be evaluated and appropriate counter-retroction measures should be initiated, if necessary, the infusion should be stopped. The remaining part of the solution should be kept for investigation if deemed necessary. Report suspicious adverse reactions Report suspicious adverse reactions after the authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows to continue monitoring the balance of benefits/risks of the medicinal product. Health professionals are asked to report any suspicious adverse reaction through the yellow card scheme. Website: www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcardThe general adverse effects of sodium excess on the body include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, thirst, reduction of salivation and lacrymation, sweating, fever, tachycardia, hypertension, renal failure, peripheral and lung oedema, respiratory arrest, headache, dizziness, irritability of the body. An excessive volume of sodium chloride 0.9% can lead to hypernatraemia (which can lead to CNS demonstrations, including seizures, coma, brain edema and death) and sodium overload (which can lead to central and/or peripheral edema) and should be treated by an assistant specialist doctor. Excessive chloride in the body can cause a loss of bicarbonate with an acidifying effect. When Sodium Chloride 0.9% is used as a diluent for injecting other medications, the signs and symptoms of overfusion relate to the nature of the additives used. In the event of accidental infusion, the treatment should be suspended and the patient should be observed for appropriate signs and symptoms related to the administered medication. Relevant and support measures should be provided where necessary. Pharmacotherapeutic Group: "Other Solution IV Additives"ATC Code: B05XXSodium Chloride 0.9% intravenous infusion is an isotonic solution, with an approximate osmolarity of 308 mOsm/l. The pharmacodynamic properties of the solution are those of sodium ions and chloride to maintain liquid and electrolyte balance. Ions, such as sodium, circulate through the cell membrane, using various transport mechanisms, including the sodium pump (Na-K-ATPase). Sodium plays an important role in neurotransmission and cardiac electrophysiology, and also in its renal metabolism. Sodium is predominantly excreted by the kidney, but there is extensive renal reabsorption. Small amounts of sodium are lost in feces and sweat. The safety of sodium chloride in animals is not relevant in view of its presence as a normal component in animal and human plasma. Water for injections. As with all parenteral solutions the compatibility of additives with the solution must be evaluated before added. In the absence of compatibility studies, this solution should not be mixed with other medicinal products. Additives known as incompatible should not be used. See section 6.6 for further instructions on the use of the product with additives Life of the packaging shelf: bag of 50 ml: 15 months100 ml bag: 2 years250 and 500 ml bags: 2 years 1000 ml bags: 3 years Life of shelf: additives. The chemical and physical stability of any additive in the pH of Sodium Chloride 0.9% Intravenous infusion in the Viaflo container must be established before use. From a microbiological point of view, the diluted product must be used immediately unless dilution has occurred in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. If not used immediately, the time and storage conditions in use are user responsibility.50 and 100 ml bags: Do not store more than 30°C.250, 500 and 1000 ml bags: This medicinal product does not require special storage conditions. Bags: 50, 100, 250, 500 or 1000 mL The bags known as Viaflo are composed of polyolefin/polyamide coextruded plastic (PL-2442). The bags fly over with a protective plastic bag composed of polyamide/polipropylene. Package sizes:- 50 bags of 50 ml per carton- 75 bags of 50 ml per carton- 1 bag of 50 ml- 50 bags of 100 ml per carton- 60 bags of 100 ml per cardboard- 1 bag of 100 ml- 30 bags of 250 ml per cardboard- 1 bag of 250 ml- 20 bags of 500 ml per cardboard- 1 bag of 500 ml- 10 bags of 1000 ml per box of 1000 ml See section 4.2 for information on the method of administration. Before adding a medication, check that it is soluble and stable in water in the pH range of the Sodium Chloride solution 0.9% Intravenous Infusion. Additives can be introduced before infusion or during infusion through the injection site. It is the responsibility of the doctor to judge the incompatibility of an additive medication with the Sodium Chloride solution 0.9% Intravenous Infusion checking the change of eventual color and/or eventually precipitate, insoluble complexes or crystal appearance. Instructions for the use of the medication to be added should be consulted. When used additive, check the isotonic before the parenteral administration. It is mandatory to mix aseptico torto and careful of any additive. Additive-containing solutions should be used immediately and not stored. Adding another medication or using an incorrect administration technique could cause fever reactions due to the possible introduction of pirogens. In case of adverse reaction, the infusion must be stopped immediately. Discuss after a single use. Discuss after a single use. Discuss any unused part. Discuss any unused part. Do not reconnect partially used bags. Do not reconnect partially used bags. Do not remove the overwrap unit until it is ready for use. The internal bag maintains the sterility of the product. Do not remove the overwrap unit until it is ready for use. The internal bag maintains the sterility of the product. Instructions for use Opening • Remove the Viaflo container from the envelopepouch right before use. • Check the minutes leaks by tightening the inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution, as sterility can be damaged • To consult the solution for the peer and absence of foreign matter. If the solution is not clear or contains foreign matter, download the solution. Preparation for management Use sterile material for preparation and administration. • Suspend container of the eyelet support. • Remove plastic protector from the output port at the bottom of the container: or grab the small wing on the port's neck with a grip of making the large wing on the lid with the other hand and the torsion, or the cap will turn off. • Use an aseptic method to configure the infusion. • Attached administration package. See the addresses of the accompanying set for the connection, the priming of the set and the administration of the solution. . Additive medicine injection techniques Warning: Additives may be incompatible. To add medicines before administration • Disinfect the drug site. • Using 19-calibre needle syringe (1.10 mm) to 22 calibers (0.70 mm), sealable drug and injection port puncture. • Mix the solution and medication thoroughly. For high-density medicines such as potassium chloride, gently touch the ports while the ports are straight and mix. Caution: Do not store bags containing added medicines. To add medicines during administration • Close the clamp on the set • Disinfect the drug site. • Using 19-calibre needle syringe (1.10 mm) to 22 calibers (0.70 mm), sealable drug and injection port puncture. • Remove the container from pole IV and/or return to a vertical position. • Evacuate both ports gently touching while the container is in vertical position. • Mix the solution and medication thoroughly. • Return container to the position of use, reopen the clamp and continue administration. Baxter Healthcare Ltd.Caxton Way, ThetfordNorfolk IP24 3SEUnited KingdomPL 00116/0334 First authorization date: 10 May 2001 Last renewal date: 19 March 2006 Dec 2018 Last update on emc: 24 Dec 2018 Company contact information Baxter Healthcare LtdCaxton Way, Thetford, Norfolk, IP24 3SE, UK+44 (0)1635 2060 +44 (0)1635 206345+44 (0)1635 206071 Bookmark this medication To mark a medicine you must register and register. Send this medication To send an email to a medicine you must register and log in. See changes in medicine To see changes in a medicine you must register and log in. This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you agree with our policy on the use of cookies.
B. Braun 0.9% Sodium Chloride Inj. B.P, 20ml | Antiseptics & Disinfectants | First Aid | Health | Guardian Singapore

Sodium Chloride 0.9% W/v, Packaging Size: 100 And 1000 ml, | ID: 19920719912
Discover B.Braun Sodium Chloride 0.9% Irrigation Sol – PinkPharm

Sodium Chloride 0.9% for Injection

B|BRAUN NaCL 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection B.P. 20x10ml | Alcare Pharmaceuticals Pte Ltd
Infusion Sodium Chloride 0.9% NACL (100ML) | Shopee Malaysia

I.V Fluids – Yeap Medical

Sodium Chloride Injection 0.9% | Applications

Dextrose 5% IV W/Sodium Chloride 0.9% 500ml | Alcare Pharmaceuticals Pte Ltd
Discover B.Braun Sodium Chloride 0.9% Saline – PinkPharm

BRAUN SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.9% 100ML(3615469)

0.9% Sodium Chloride – Golden Horse Medical Supplies

Sodium Chloride 0.9% (Normal Saline), USP, Sterile Grade, Intermountain | Fisher Scientific

Golden Queen Cosmetics | High Quality Massage Oil and Essential Oil
Rinscap Ns Sodium Chloride 0.9% for Irrigation Solution BP 500ml

Baxter NaCl 0.9% Sodium Chloride (Saline) For Irrigation. One Litre (1000ml).: Amazon.co.uk: Health & Personal Care

SODIUM CHLORIDE INJECTION USP 0.9% - Teligent Canada

Sodium chloride nacl 0.9% saline on Carousell
Braun Sodium Chloride NacI 0.9% (20ml x20 pcs /box) - BW Generation Adult Diapers

Sodium Chloride Saline 0.9% IV Infusion Kabipac 250ml - Henry Schein Dental

Sodium Chloride 0.9% , Packaging Size: 500 And 1000 ml, | ID: 19920352573
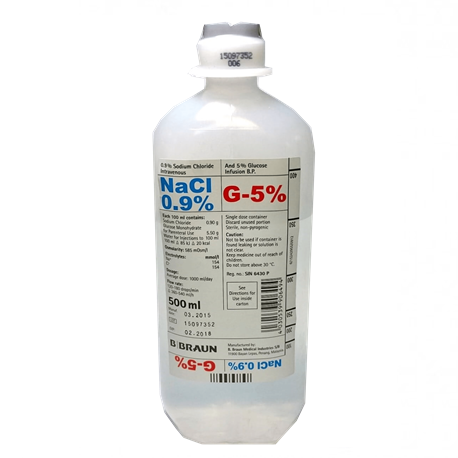

Buy B Braun Sodium Chloride 0.9%, Glucose 5% intravenous infusion injection, 500ml Online at Best Price | Lumiere32.sg

SODIUM CHLORIDE (Generic) Irrigation Solution 0.9%, 500-mL - Chewy.com
Infusol NS Sodium Chloride 0.9% W/V (100ml / 250ml / 500ml / 1000ml) | Shopee Malaysia

Sodium Chloride Irrigation 0.9% - 500 ml - Canadian Safety Supplies

Sodium Chloride 0.9%, Glass 9mg/mL, SDV, 100mL Vial | McGuff Medical Products

Sodium Chloride Saline 0.9% IV Infusion Kabipac 1 Litre - Henry Schein Special Markets
Baxter Sodium Chloride 0.9% for Irrigation 500Ml Bottle - Adam Dental Supplies Australia

Buy RinsCap Normal Saline Sodium Chloride 0.9% Irrigation Solution BP - 500ml Online at Best Price | Lumiere32.sg

Sodium Chloride IV 0.9% - 10mls - Openhouse Products
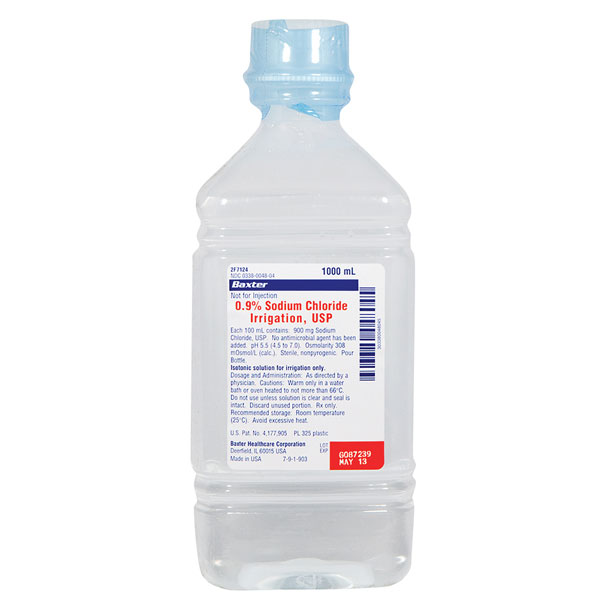

Baxter 0.9% Sodium Chloride Irrigation - 1000 mL USP Plastic Pour Bottle | Dental Supplies
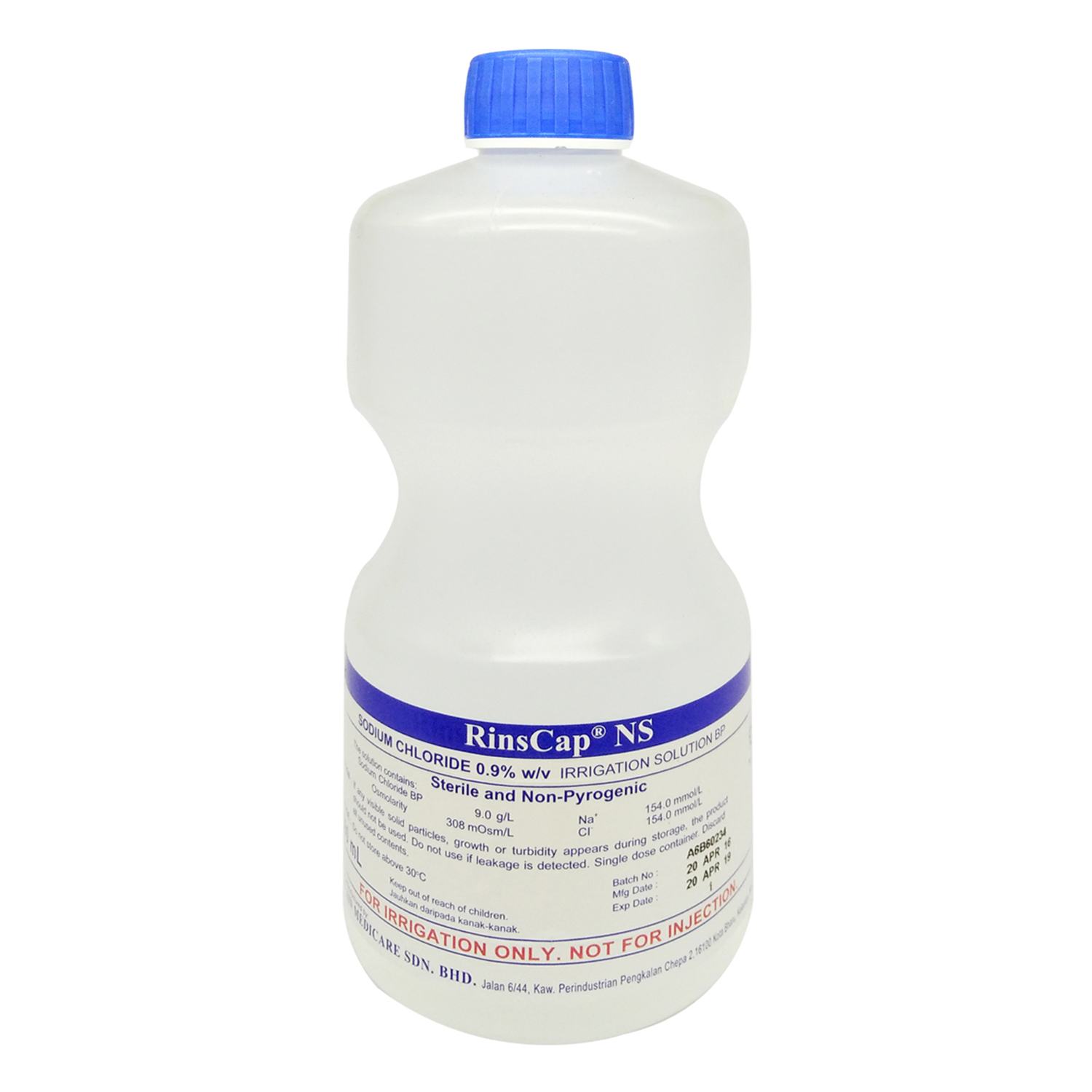

Rinscap Ns Sodium Chloride 0.9% For Irrigation Solution Bp 1l - Alpro Pharmacy
Sodium Chloride 0.9% - Normal Saline 500Ml Iv Freeflex Bag | AIMS MEDICAL
Euro-Med Sodium Chloride 0.9% IV - Joyson Pte Ltd | Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices Distributor | The Joy of Living

Sodium Chloride 0.9% Rx

Sodium Chloride 0.9% W/v, Packaging Size: 100 And 1000 ml, | ID: 19920719912
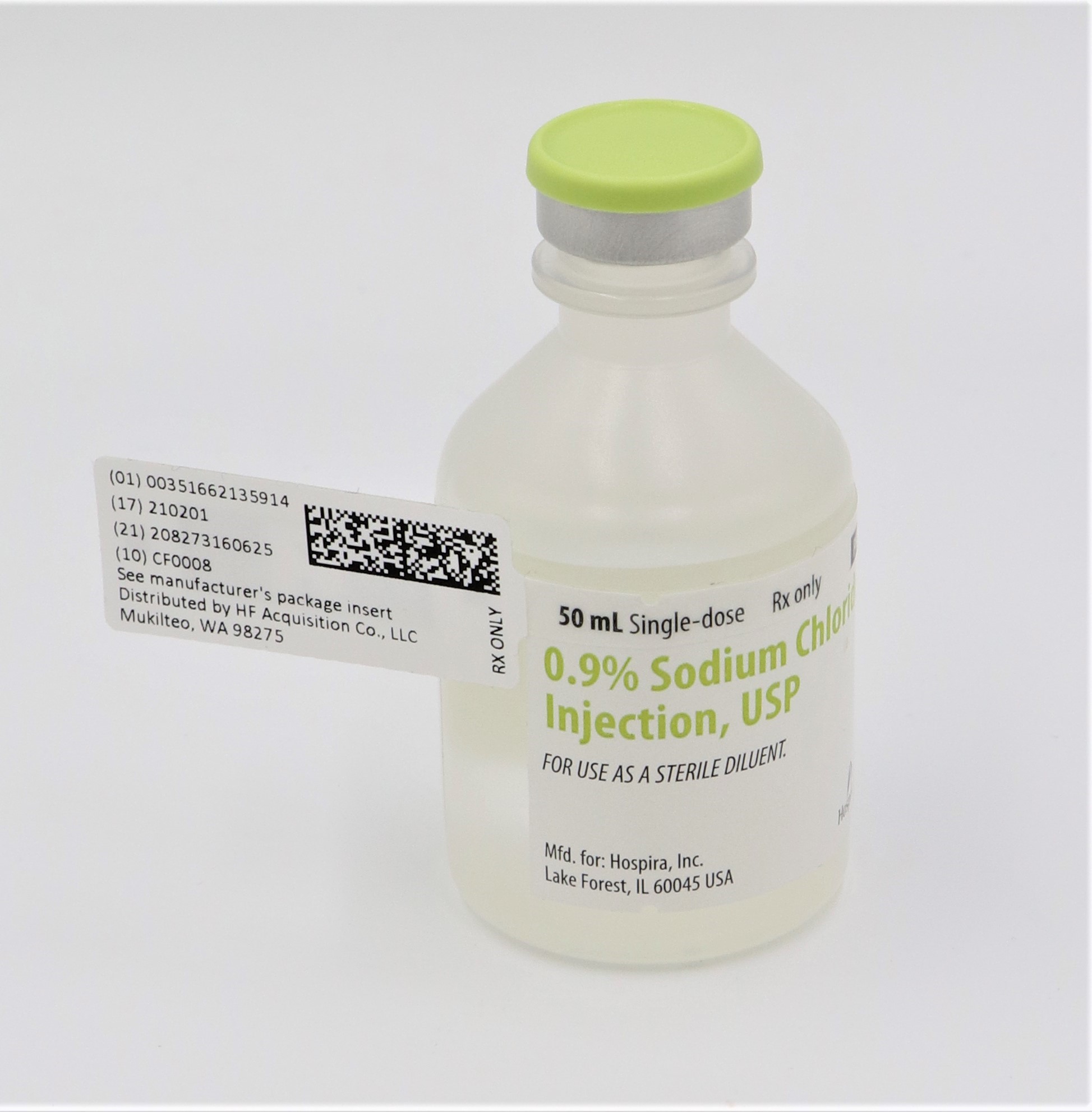
0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE INJECTION, USP 50mL VIAL
5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection by ICU Medical | Medline Industries, Inc.

Baxter 0.9% Sodium Chloride Irrigation - 500 mL USP Plastic Pour Bottle | Dental Supplies
Posting Komentar untuk "sodium chloride 0.9%"